阅读数:10071
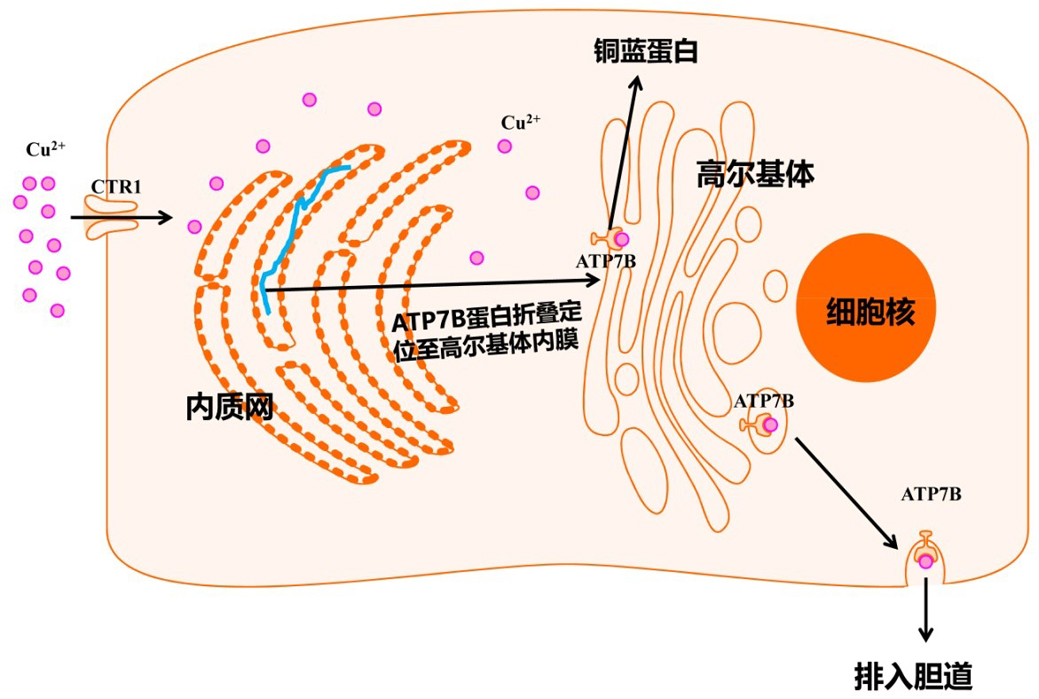
肝豆状核变性是一种常染色体隐性遗传疾病,ATP7B是目前已知的唯一相关致病基因。ATP7B基因主要在肝细胞中表达,经内质网、高尔基体修饰加工后定位至高尔基体内膜,参与铜蓝蛋白的合成和铜的胆道排泄。当机体铜过量时,高尔基体以囊泡的形式向细胞膜转移,与细胞膜融合后将铜排到胆道。
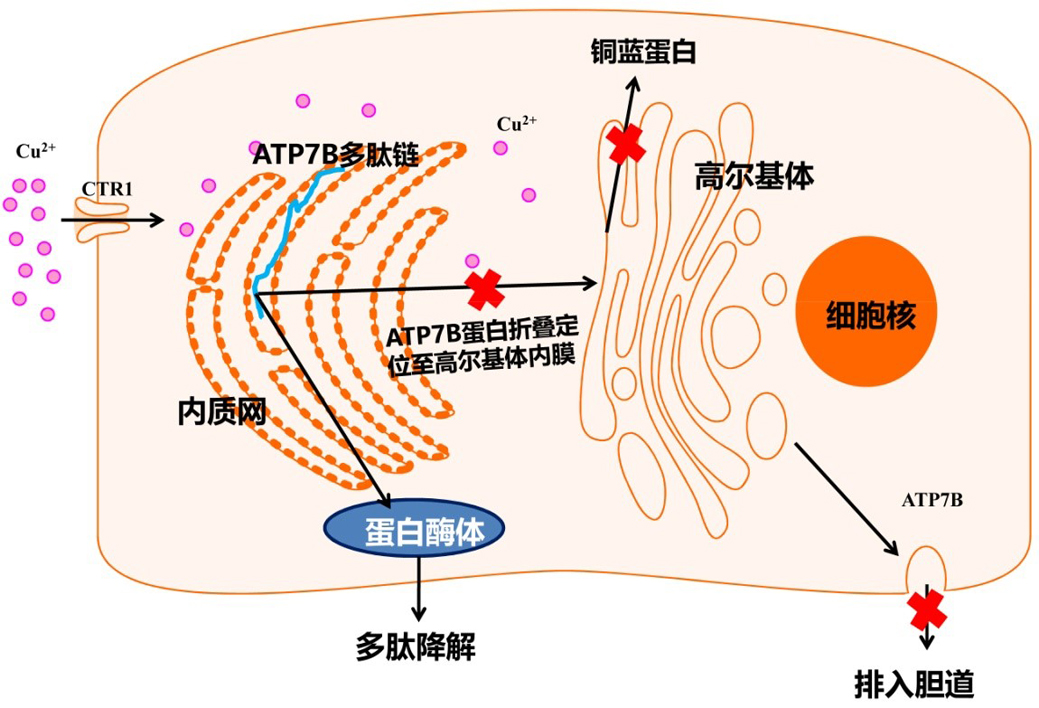
当ATP7B发生突变时,5'UTR区的突变会导致ATP7B的转录受到影响,无义、移码和剪切位点的突变常导致ATP7B翻译一个截短的ATP7B多肽链,而错义突变常导致蛋白折叠加工及细胞定位受阻,突变蛋白进入溶酶体降解,铜蓝蛋白合成障碍,胆道排铜出现障碍。
参考文献
1. Członkowska A, Litwin T, Dusek P, Ferenci P, Lutsenko S, Medici V, et al. Wilson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:21.
2. Chesi G, Hegde RN, Iacobacci S, Concilli M, Parashuraman S, Festa BP, et al. Identification of p38 MAPK and JNK as new targets for correction of Wilson disease-causing ATP7B mutants. Hepatology. 2016;63:1842–59.
3. Harada M,, Sakisaka S, Terada K, Kimura R, Kawaguchi T, Koga H, et al. A mutation of the Wilson disease protein, ATP7B, is degraded in the proteasomes and forms protein aggregates. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:967–74.